The steps of dilution method to detect BOD5 in water
发布时间:2021/5/24 9:12:37 来源:贯奥仪器仪表 作者:便携式多参数水质分析仪器 阅读次数:
Generally BOD5 (five-day biochemical oxygen demand) is commonly used by the dilution method. The original sample or the appropriately diluted sample is selected for determination, and then diluted with an appropriate multiple. So that there is enough dissolved oxygen in the culture flask to meet the aerobic requirements of the five-day biochemical. Divide the samples that meet the above conditions into two, one for measuring the mass concentration of dissolved oxygen on the day, and the other for measuring the mass concentration of dissolved oxygen after 5 days of incubation in an incubator at 20 degrees Celsius. The difference between these two samples is the five-day biochemical oxygen demand.
For some seriously polluted surface water, most industrial wastewater and domestic sewage, because it contains more organic matter, it needs to be diluted and then cultured and measured to reduce its concentration and ensure that the biodegradation process is carried out under the condition of sufficient dissolved oxygen. The specific dilution factor of the water sample can be calculated with the help of potassium permanganate index or chemical oxygen demand (COD).
For industrial wastewater that contains no or less microorganisms, inoculation should be carried out when measuring BOD to attract microorganisms that can decompose organic matter in the wastewater. When the wastewater contains organic matter that is difficult to be degraded by the microorganisms in general domestic sewage at a normal speed or contains highly toxic substances, it should be inoculated with domesticated microorganisms.

Instruments and reagents used in the dilution method
(1) Constant temperature biological incubator, 20L thin-mouth glass bottle, 1000mL measuring cylinder, glass stirring rod (the length of the rod should be 20cm longer than the height of the measuring cylinder, and a diameter slightly smaller than the diameter of the measuring cylinder is fixed at the bottom of the rod, and there are several Hard rubber plate with small holes), 200~300mL dissolved oxygen bottle, siphon (for aliquoting water samples and adding dilution water).
(2) Phosphate buffer solution Dissolve 8.5g potassium dihydrogen phosphate KH2PO4, 21.75g dipotassium hydrogen phosphate K2HPO4, 3.4g disodium hydrogen phosphate Na2HPO·7H2O and 1.7g ammonium chloride NH4Cl in water and dilute to 1000mL. The pH of this solution is 7.2.
(3) Magnesium sulfate solution Dissolve 22.5g of magnesium sulfate MgSO4·7H2O in water and dilute to 1000mL.
(4) Calcium chloride solution Dissolve 27.5g of anhydrous calcium chloride in water and dilute to 1000mL.
(5) Ferric chloride solution Dissolve 0.25g of ferric chloride FeCl3·6H2O in water and dilute to 1000mL.
(6) Fill a certain amount of distilled water in a 20L glass bottle for dilution water, add 1 mL of calcium chloride solution, ferric chloride solution, magnesium sulfate solution, and phosphate buffer solution to each liter of distilled water, and then use an oil-free air compressor or Membrane pump aeration, when the dissolved oxygen content in the water reaches 8-9mg/L, stop the aeration and cover tightly to stabilize the dissolved oxygen.
If the industrial wastewater contains toxic substances and lack of microorganisms, the dilution water should be added with appropriate amount of sedimented domestic sewage as the inoculation of microorganisms, usually 2mL of sedimentation sewage per liter of dilution water; or introduce special domesticated microorganisms into the water sample Vaccination in.
(7) All reagents for measuring dissolved oxygen.

Operation steps for detecting BOD5 in water by dilution method
1. Inspection of dilution water
Use the siphon method to suck the dilution water (or inoculate the dilution water), fill the two dissolved oxygen bottles, stop them, and seal them with water. One of the bottles was immediately measured for dissolved oxygen, and the other was placed in a constant temperature biological incubator, and measured after 5d incubation at (20±1)℃. The reduction of dissolved oxygen is required to be less than 0.2~0.5mg/L.
2. Determination of the dilution factor
Surface water can be obtained by multiplying the measured permanganate index by an appropriate coefficient to obtain the dilution factor.
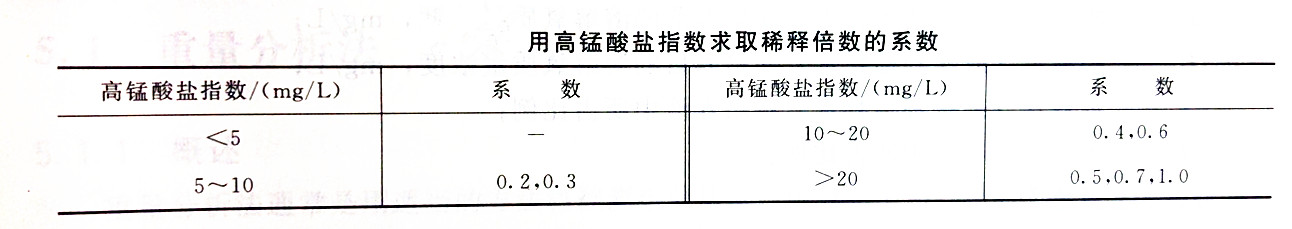 Industrial wastewater can be determined by the COD value measured by the dichromate method. Usually three dilution ratios are required, that is, when using dilution water, the COD value is multiplied by the coefficients 0.075, 0.15, and 0.225 respectively to obtain three dilution multiples. When using the inoculation dilution water, they are multiplied by 0.075, 0.15 and 0.25 respectively. Obtain three dilution multiples.
If there is no readily available permanganate index or COD value data, generally more polluted wastewater (such as industrial wastewater) can be diluted to 0.1% to 1%, and for ordinary and precipitated wastewater, it can be diluted to 1% to 5%. The effluent after biological treatment can be diluted to 5%~25%, and the polluted river water can be diluted to 25%~100%
Industrial wastewater can be determined by the COD value measured by the dichromate method. Usually three dilution ratios are required, that is, when using dilution water, the COD value is multiplied by the coefficients 0.075, 0.15, and 0.225 respectively to obtain three dilution multiples. When using the inoculation dilution water, they are multiplied by 0.075, 0.15 and 0.25 respectively. Obtain three dilution multiples.
If there is no readily available permanganate index or COD value data, generally more polluted wastewater (such as industrial wastewater) can be diluted to 0.1% to 1%, and for ordinary and precipitated wastewater, it can be diluted to 1% to 5%. The effluent after biological treatment can be diluted to 5%~25%, and the polluted river water can be diluted to 25%~100%
3. The preparation of diluted water samples and BOD determination must not be left
(1) There is no need to measure the diluted water sample. The surface water with higher dissolved oxygen content and less organic content can be directly transferred to the two dissolved oxygen bottles by siphoning without dilution. The transfer process Care should be taken not to generate bubbles in the medium. Use the same operation to make the two dissolved oxygen bottles overflow a little after being filled with water samples, and stoppered with water.
Then immediately measure the dissolved oxygen in one of the bottles. Put the other bottle in the incubator and incubate at (20±1)℃ for 5 days. Measure its dissolved oxygen.
(2) Need to be measured by diluted water sample
①General dilution method
According to the selected dilution ratio, use the siphon method to introduce part of the dilution water (or inoculation dilution water) along the cylinder wall into the 1000mL graduated cylinder, add the required amount of uniform water sample, and then introduce the dilution water (or inoculation dilution water) to 1000mL, Use a glass rod with a rubber plate to stir up and down carefully. When stirring, do not expose the rubber plate of the stir bar to the water surface to prevent bubble.
According to the determination procedure of the undiluted water sample, bottling was carried out, and the dissolved oxygen content of the day and the dissolved oxygen content after 5 days of culture was measured. The general dilution method is usually used for diluted water samples with water samples below 1%.
②Direct dilution method
The direct dilution method is to directly dilute in the dissolved oxygen bottle. In two known dissolved oxygen bottles with the same volume (the difference is less than 1mL), add part of the dilution water (or inoculation dilution water) by siphoning, and then add the water sample amount calculated according to the bottle volume and the dilution ratio, and then introduce Dilute the water (or inoculate the dilution water) until it is just full, stopper, and do not leave bubbles in the bottle. The rest of the operation is the same as the above dilution method.
In BOD5 determination, sodium azide correction method is generally used to determine dissolved oxygen. In case of interfering substances, other determination methods should be used according to the specific situation.
Finally, calculate and process according to the obtained data, and the water sample directly cultured without dilution can be calculated by the formula: BOD5(mg/L)=C1-C2. The diluted cultured water sample can be calculated by the formula: BOD5 (mg/L)=(C1-C2)-(B1-B2)f1/f2.

Problems needing attention when detecting BOD5 in water by dilution method
(1) For the water after biochemical treatment often contains nitrifying bacteria, which interferes with the determination of BOD, nitrification inhibitors, such as allyl thiourea C4H3N2S, or acid treatment can be added to eliminate the interference.
(2) In samples with two or three dilution ratios, where the consumption of dissolved oxygen is greater than 2 mg/L and the remaining dissolved oxygen is greater than 1 mg/L, both are valid. When calculating the results, the average value should be taken.
(3) During the cultivation process, check the sealing water of the culture flask frequently and replenish it in time to avoid drying up.



