The heavy metal cadmium in the water mainly comes from the mining of different minerals, such as coal mines, aluminum mines and copper mines. In practical applications, cadmium detection methods mainly use atomic absorption methods, such as direct inhalation flame atomic absorption method, extraction flame atomic absorption method and graphite furnace atomic absorption method. Among them, direct inhalation of flame atomic absorption method is relatively simple to operate, so today we will talk about how to use this method to detect heavy metal cadmium in water.
In this method, the water sample or the digested sample is directly sucked into the flame, and the atomic vapor formed in the flame absorbs the characteristic electromagnetic radiation emitted by the light source. Compare the measured absorbance of the sample with the absorbance of the standard solution, and then determine the cadmium content in the water.

1. Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer
2. Background correction device
3. Element lights
4. Nitric acid
5. Perchloric acid
6. Gas
7. Purity Acetylene
8. Metal standard stock solution
a. Standard stock solution of cadmium and zinc
Accurately weigh 0.5000g of spectrally pure metal cadmium and metal zinc after washing and drying with dilute acid, dissolve it with 50mL of nitric acid (1+1), and heat if necessary until the dissolution is complete. Dilute to 500.0mL with tertiary reagent water.
b. Copper standard stock solution
Accurately weigh 0.2500g of spectrally pure copper that has been cleaned with dilute acid and dried, dissolved in 50mL of (1+1) nitric acid, and heated if necessary until it is completely dissolved and diluted to 100.0mL with tertiary reagent water.
c. Lead standard stock solution
Accurately weigh 0.5000g of spectrally pure metallic lead that has been cleaned with dilute acid and dried, dissolved in 50mL of (1+1) nitric acid, and heated if necessary until it is completely dissolved and diluted to 100.0mL with tertiary reagent water.
9. Mixed standard solution
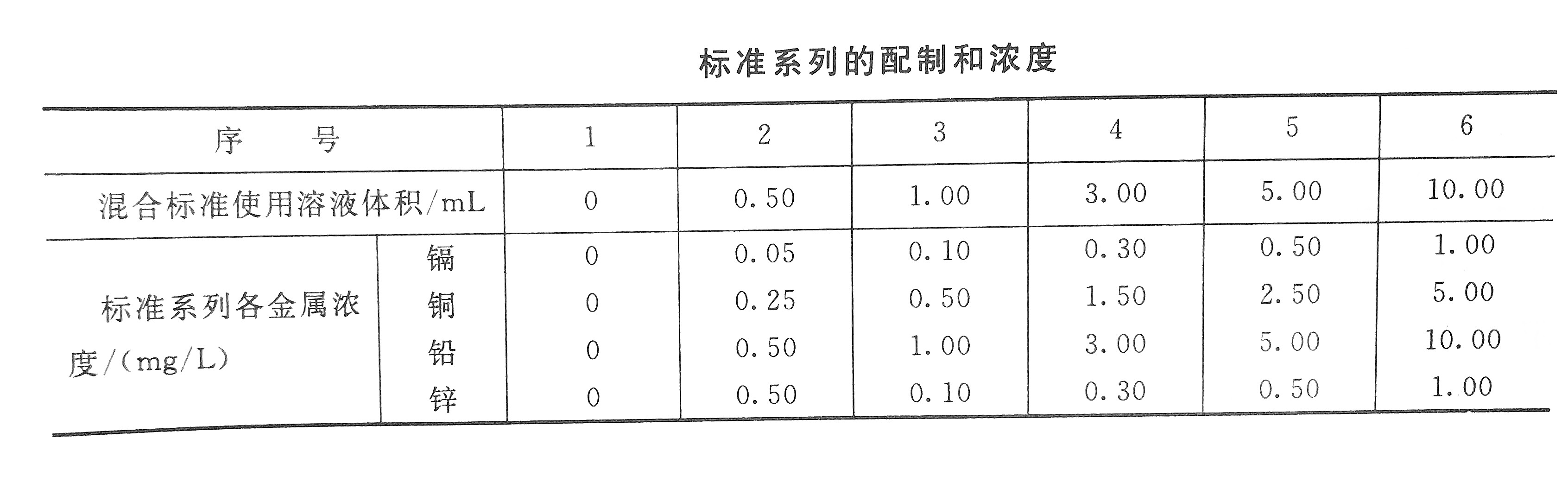
Take 5mL of cadmium and zinc standard stock solutions, and 10mL of copper and lead standard stock solutions in the same 500mL volumetric flask and dilute to the mark with 0.2% nitric acid. The prepared mixed standard solution contains 10.0ug, 50.0ug, 100.0ug and 10.0ug per milliliter of cadmium, copper, lead and zinc, respectively.
Take 100mL of water sample into a 200mL beaker, add 5mL of nitric acid, heat and digest on a hot plate (do not boil), steam to about 10mL, add 5mL of nitric acid and 2mL of perchloric acid, continue to digest until about 1mL. If the digestion is not complete, add 5mL of nitric acid and 2mL of perchloric acid, and steam again to about 1mL. Remove and cool, add third grade reagent water to dissolve the residue, and dilute to 100mL.
Take 100mL of 0.2% nitric acid, operate according to the same procedure as above, and use this as a blank sample.
Select the analysis line and adjust the flame according to the relevant parameters. The instrument was zeroed with 0.2% nitric acid, the blank sample and the sample were sucked in, and the absorbance was measured. After deducting the absorbance of the blank sample, find out the concentration of metal cadmium to be measured in the sample from the calibration curve. If possible, you can also read the concentration of metal cadmium to be measured in the sample directly from the instrument.
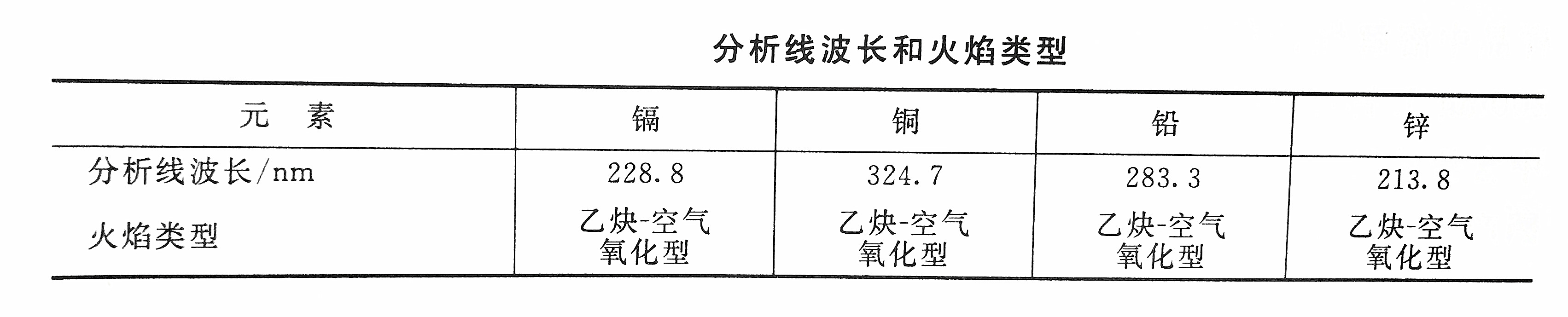
Draw the mixed standard solution according to the standard concentration configuration table, put them into 6 100mL volumetric flasks, and dilute with 0.2% nitric acid to a constant volume. Then measure the absorbance according to the steps of sample determination, plot the corresponding concentration with the absorbance of each standard after blank correction, draw a calibration curve, and finally calculate the content of the measured metal cadmium according to the corresponding formula.
最新动态
相关推荐